Mobilize Power: The world's first vehicle-to-grid product for end customers
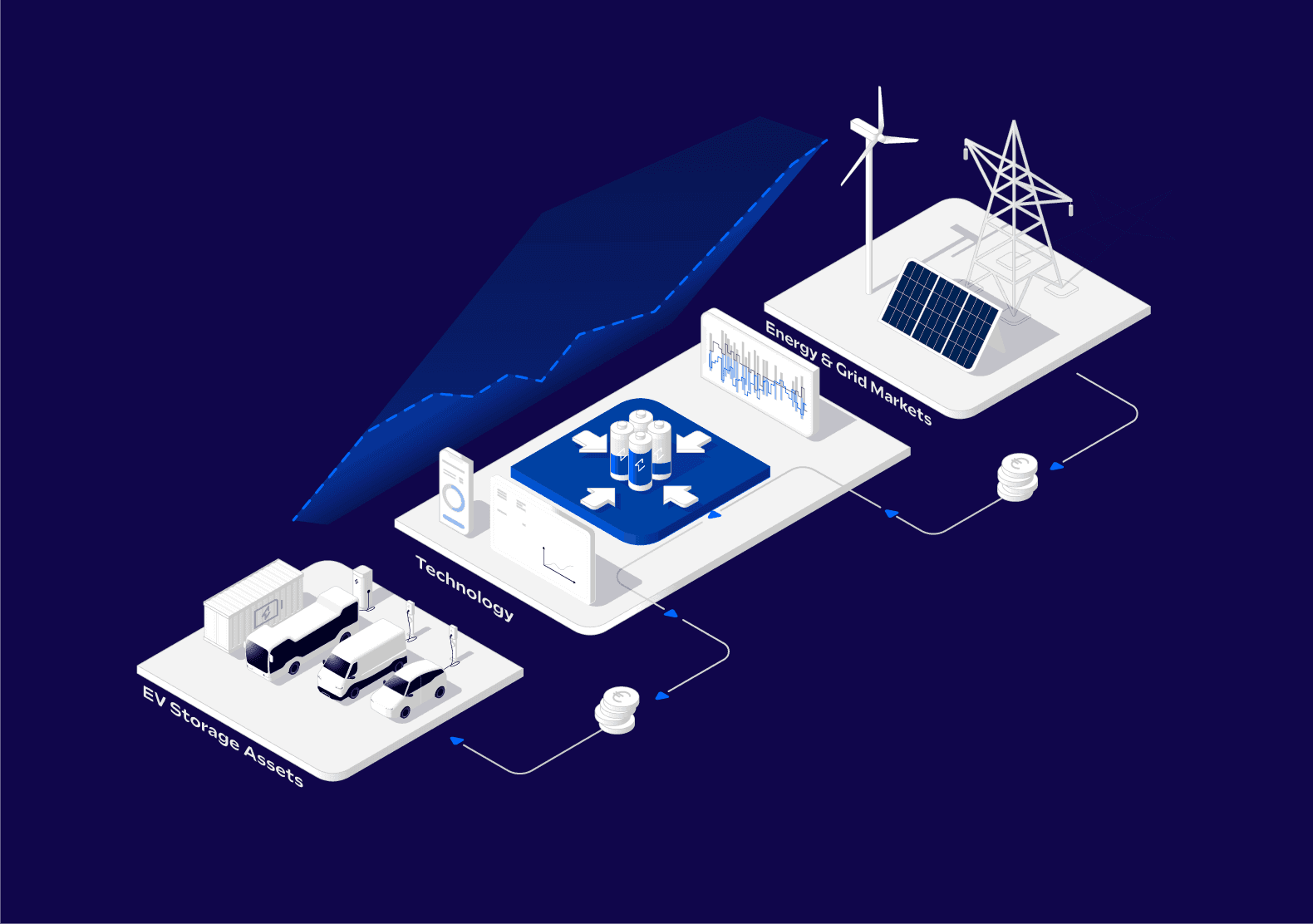
How our technology works
Our technology consists of the Flexibility Aggregator, which bundles the batteries into a virtual power plant, and the Flexibility Trader. The coordinated systems interact optimally, aggregating the storage potential of the vehicles and marketing the “flexibilities” in a way that benefits the system and generates profit. The storage capacity provided in this way is an important building block on the path to a renewable energy system.
We analyze customers' charging needs and battery status in real time. This allows us to determine when and how the car is available.
The flexibility of many electric vehicles is bundled by our aggregation platform and made available to the energy system as a virtual power plant.
Our platform sells and buys electricity specifically where it is most valuable: on day-ahead, intraday auction, and intraday continuous markets. Through this multi-market optimization, we achieve values that are over 300% higher than those achieved through single-market optimization.
We give each car individual instructions: it is charged or discharged – always with an eye on electricity prices, grid demand, and battery life.
Thanks to this intelligent control system, peak loads, grid expansion costs, and redispatch measures are reduced. This not only saves money, but also strengthens the integration of renewable energies.
Components of the V2G product
Our product consists of

Vehicle
Currently compatible models include: Renault R5 E-Tech, Renault R4 E-Tech, Renault Megane E-Tech, Renault Scenic E-Tech and Alpine A290 . More models may be added in the future.
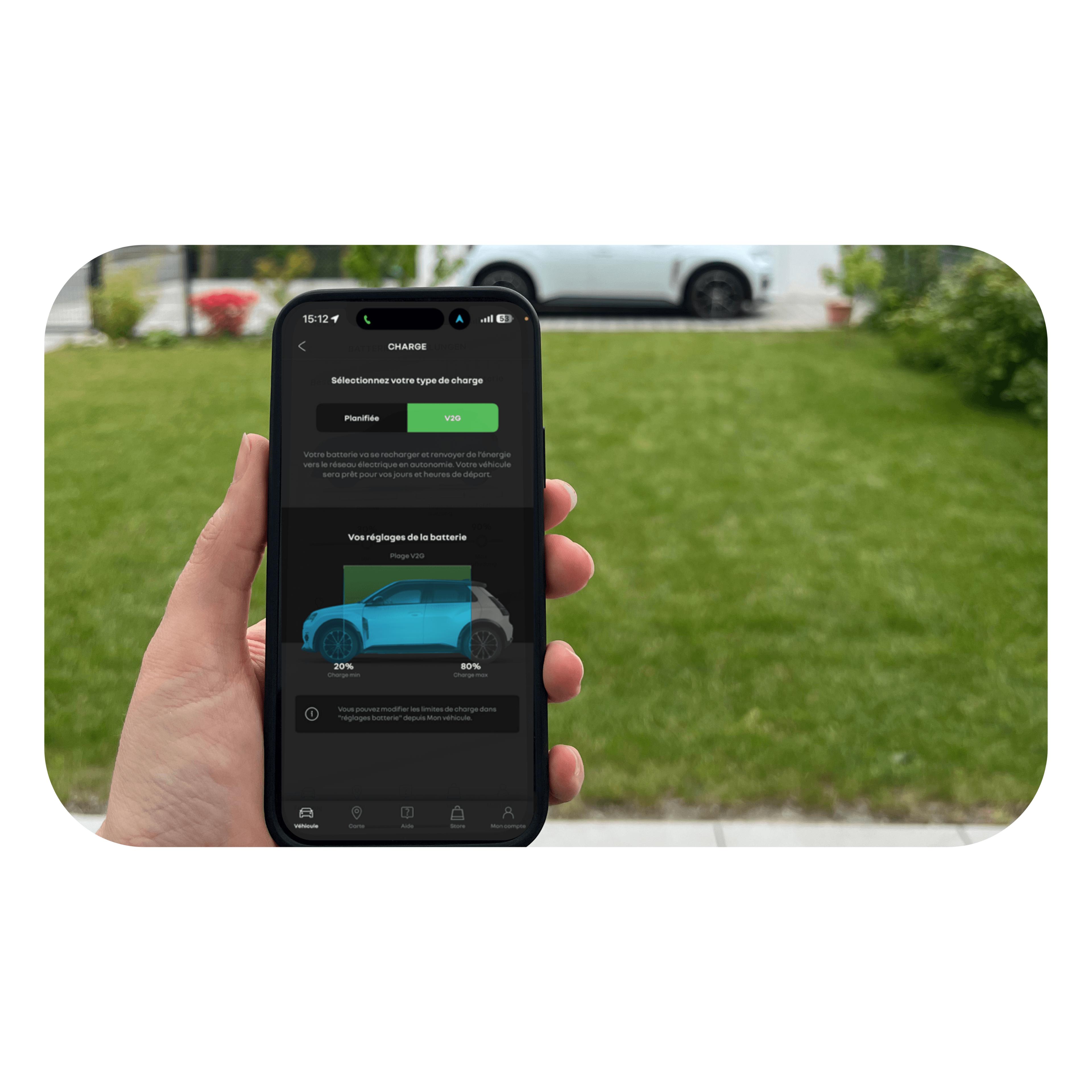

App
Using the My Renault app, drivers can enter their desired charge level and departure time and view their V2G savings.

Bidirectional wallbox
The Mobilize PowerBox Verso (AC wallbox) enables V2G charging. Standard unidirectional charging is also possible and compatible with all vehicles. Charging station made in Europe.

Electricity tariff & marketing
Green electricity contract with The Mobility House for vehicle and home, including a 1-year price guarantee. Flexibility trading runs in the background.
Wheels offer the largest storage capacity
Electric cars are game changers in the energy market: they are not only becoming the largest load, but also the largest battery of our time. This is because they spend 90% of their service life simply standing around, waiting to be used as flexible storage. Even today, the batteries of 1.65 million electric cars have a storage capacity of 100 GW, around 10 times the current output of German pumped storage power plants1. This represents enormous, as yet untapped potential.
1) According to data from Fraunhofer ISE, the installed capacity of all pumped storage power plants in Germany at the end of 2024 was around 10 GW.
Why did we launch Mobilize Power in France first?
Because the conditions are right here.
Renault has recognized the potential of electric cars—and has taken the next step together with us: with the world's first V2G product.
France has centralized grid structures and nationwide smart meters in its energy market—perfect conditions for thinking big about V2G.
New savings opportunities attract new customers. The Renault R5 opens up new opportunities and enables free charging, which in turn ensures long-term customer loyalty.

Customers drive 10,000 km per year free of charge
Our vision of customers charging for €0 – zero zero – has become a reality with this tariff.
Mobilize Power customers collect so-called “V2G Hours” for each hour of charging and returning the vehicle, which are credited to their electricity bill as a bonus. Those who plug in their vehicle for 16 hours a day benefit from savings of €600 per year.
Advantages for automotive manufacturers
We provide the technology, automotive manufacturers (OEMs) provide the service.
Job split according to desired depth of value creation – from energy tariffs to hardware to installation, optionally selectable
OEMs benefit from our industry-leading trading capabilities for maximum returns.
Lower operating costs for customers make electric cars even more competitive right now.

How far has vehicle-to-grid progressed in other countries?
|
Country |
V2G product / project |
OEM (V2G capable) |
EVSE |
Regulatory framework & conditions |
|
UK |
Octopus Power Pack (Beta, since 2025) |
BYD |
Bidi Charger expensive |
Double Taxation, no clear V2G tariffs |
|
France |
Mobilize Power (Renault, Mobilize, The Mobility House) |
Renault 5, Alpine A290 |
PowerBox Verso (bis 22 kW) |
Clear setting, fast Smart-Meter rollout, centralized grid (Enedis) |
|
The Netzerlands |
We Drive Solar (with Utrecht, Renault, MyWheels, Hyundai) |
Nissan Leaf, Hyundai Ioniq 5 |
We Drive Solar AC Charger |
Double energy taxation stays a topic |
|
Japan |
Nissan Energy Share (for companies, municipalities, fleet) |
Nissan (V2G-ready, very active) |
CHAdeMO standard |
Clear standards, V2H established, V2G only integrated to a limited extent |
Sources: electrive.net,industrialnews.co.uk,wedrivesolar.com
How can V2G also be implemented in Germany?
In order for Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) to reach its full potential, the political and regulatory course must be set now. The following measures are necessary to achieve this:
- The double taxation of electricity stored in vehicle batteries will finally be abolished from April 2026 – as is already the case with stationary storage systems. Learn more
- Smart meters should be implemented across the board in a customer-friendly and digital manner.
- Dynamic grid fees would create incentives to use the grid intelligently and make V2G more economically attractive and effective for the energy transition.
Several pilot projects are currently underway. The Mobility House Energy is part of the “Grids & Benefits” pilot project, which is testing grid-friendly bidirectional charging in practice under the auspices of the BMWK. Our goal: to establish V2G solutions in Germany, the UK, and other European markets and to actively shape the energy transition.
Institutions such as TÜV Germany2 have also long been calling for vehicle-to-grid to be established as an integral part of the energy transition.
2: TÜV: German mandatory vehicle inspection for safety and emissions, similar to the UK MOT test.
